Introduction
As global organisational operations continue to advance into new counties and regions, so do concerns about global data privacy compliance. In today’s digital age, organizations must take active steps to protect sensitive information and comply with global data protection laws. The consequences of failing to take a global approach to data privacy can be severe, including hefty fines, legal action, and damage to an organization’s reputation they have built up and established over many years. That’s why building a data privacy framework is essential for any organisation that handles both personal and sensitive data about individuals.
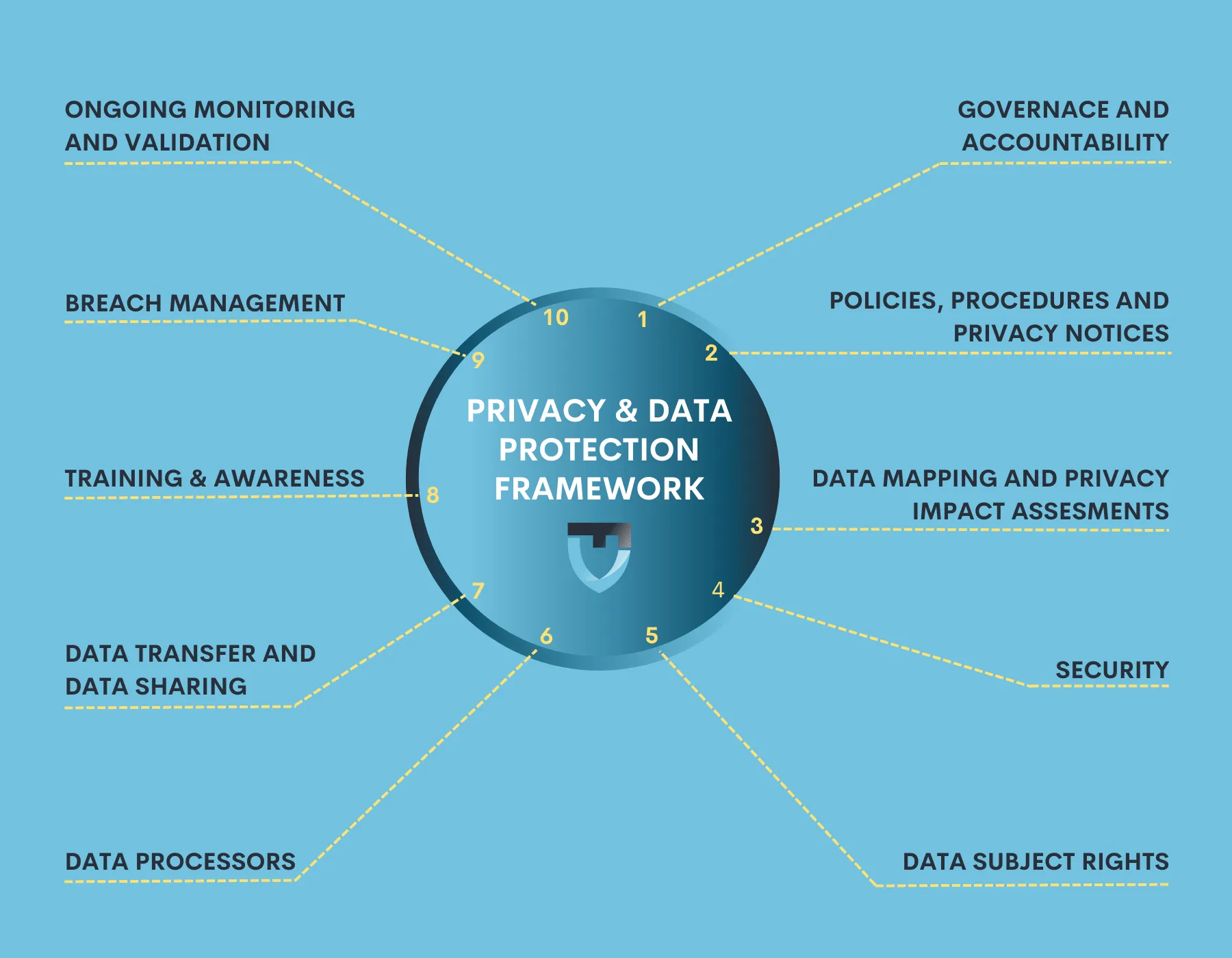
A data privacy framework is a comprehensive set of policies, processes, awareness and guidelines that govern how an organisation collects, stores, uses, and discloses data. This framework should be designed to meet global data privacy laws, such as the UK and EU GDPR, the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) in the United States, Japan APPI, Brazil LGPD and both Thailand and Singapore PDPA’s to name a few. By implementing a data privacy framework, organizations can ensure global privacy compliance with these laws and protect the sensitive information of their employees and customers.
Seven Recommended Steps in Establishing a Privacy Framework
Here are some of the ways that building a data privacy framework can help organizations stay compliant with global data protection laws:
- Identify and classify data: The first step in building a data privacy framework is to identify and classify the data that an organization collects and stores. This includes personal data, such as names, addresses, and Social Security numbers, as well as sensitive data, such as health records and financial information. By classifying data, organizations can better understand the risks associated with storing and using it and put appropriate safeguards in place. This can be achieved with a comprehensive data mapping exercise and establishment of a Record of Processing Activities (ROPA)
- Implement appropriate security measures: Organizations must implement appropriate security measures to protect personal and sensitive data from unauthorized access, theft, and other threats. This can include encryption, access controls, and regular data backups. By implementing these measures, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches and comply with global data protection laws that require organizations to take reasonable measures to protect sensitive data. This can be achieved by strengthening your Technical and Organisational Measures (TOMS) which covers both digital and logical access safeguards.
- Develop policies and procedures: A data privacy framework should include policies and procedures that govern how an organization collects, stores, uses, and discloses data. These policies and procedures should be clear and concise and should be communicated to all employees. By developing these policies and procedures, organizations can ensure that they are complying with global data protection laws and that all employees understand their roles and responsibilities in protecting sensitive data.One of the most important policies is the data handling policy, which informs employees on how to treat data as they execute their day to day duties.
- Conduct regular risk assessments: Organizations should conduct regular data maturity risk assessments and remediation actions to identify potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in their data privacy framework at least once a year. These assessments should be conducted by a third party and should include an analysis of the organization’s data collection and storage practices, as well as its policies and procedures. By conducting regular risk assessments, organizations can identify and remediate potential issues before they become significant problems.
- Train employees: Employees are often the first line of defense when it comes to data privacy. That’s why it’s essential to train employees on the organization’s data privacy policies and procedures. This training should be mandatory for all employees and should include information on how to identify and report potential data breaches, how to handle personal and sensitive data, and how to comply with global data protection laws. Also regulare awareness campaigns should be rolled out to help employees focus and keep privacy top of mind. It is said that 76% of all data breaches are caused by employee errors or poor company practices.
In an interesting Forbes article by Edward Tuorinsky he informs that compliance scores alone do not result in data breach safety but by adopting a Zero Trust Architecture Approach (ZTA) can be a major step in the right direction. But remember this can require a workforce a mindset change which we all know can take at least 66 days to set in and become part of every day operations as employees go through the six stages of change
1. Denial, optimism or skepticism
2. Resistance, fear and doubt
3. Confusion, withdrawal
4. Exploration, hope and determination
5. Commitment, confidence and acceleration
6. Understanding, ownership and new habits.
In conclusion, building a data privacy framework is essential for any organization that handles both personal and sensitive data. By implementing appropriate security measures, developing policies and procedures, conducting regular Data Maturity Risk Assessments, and regular training and awareness campaigns for employees, organizations can ensure that they are compliant with global data protection laws and protect personal and sensitive information. The results of failing to do so can be severe, so it’s essential to take data privacy seriously and build a comprehensive data privacy framework to achieve Global Privacy Compliance